Intro
As part of the Container Tools team at Red Hat I'd like to highlight a feature of Atomic App: support for execution via OpenShift's cli command oc new-app.
The native support for launching Nulecules means that OpenShift users can easily pull from a library of Atomic Apps (Nuleculized applications) that exist in a Docker registry and launch them into OpenShift. Applications that have been packaged up in a Nulecule offer a benefit to the packager and to the deployer of the application. The packager can deliver one Nulecule to all users that supports many different platforms and the deployer gets a simplified delivery mechanism; deploying a Nulecule via Atomic App is easier than trying to manage provider definitions.
DEMO Time
OK. Let's do a demo. I'll choose the guestbook example application developed by Kubernetes. The Nulecule defintion for this example lives here. To start the container in OpenShift via oc new-app you simply run the following command from the command line:
# oc new-app projectatomic/guestbookgo-atomicapp --grant-install-rights
This will run a pod using the container image projectatomic/guestbookgo-atomicapp. The Atomic App software that runs inside the container image will evaluate the Nulecule in the image and communicate with OpenShift in order to bring up the guestbook application, which also leverages redis.
You should now be able to see the redis and guestbook replication controllers and services:
# oc get rc CONTROLLER CONTAINER(S) IMAGE(S) SELECTOR REPLICAS AGE guestbook guestbook kubernetes/guestbook:v2 app=guestbook 3 3m redis-master redis-master centos/redis app=redis,role=master 1 3m redis-slave redis-slave centos/redis app=redis,role=slave 2 3m # oc get svc NAME CLUSTER_IP EXTERNAL_IP PORT(S) SELECTOR AGE guestbook 172.30.24.168 3000/TCP app=guestbook 3m redis-master 172.30.210.63 <none> 6379/TCP app=redis,role=master 3m redis-slave 172.30.62.63 <none> 6379/TCP app=redis,role=slave 3m
As well as the pods that are started as a result of the replication controllers:
# oc get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE guestbook-6gujf 1/1 Running 0 3m guestbook-m61vq 1/1 Running 0 3m guestbook-otoz4 1/1 Running 0 3m redis-master-wdl80 1/1 Running 0 3m redis-slave-fbapw 1/1 Running 0 3m redis-slave-oizwb 1/1 Running 0 3m
If you have access to the instance where the pods are running you can access it via a Node IP and NodePort, however this is not common in a hosted environment. In a hosted environment you need to expose the service in openshift via a route:
# oc expose service guestbook route "guestbook" exposed # oc get route guestbook NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICE LABELS INSECURE POLICY TLS TERMINATION guestbook guestbook-proj1.e8ca.engint.openshiftapps.com guestbook app=guestbook
Now you should be able to access the guestbook service via the provided hostname; in this case it is guestbook-proj1.e8ca.engint.openshiftapps.com. A quick visit with Firefox gives us:
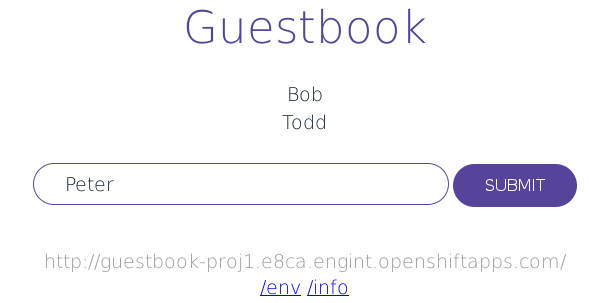
And we have a guestbook up and running!
Give oc new-app on an Atomic App a spin and give us some feeback at container-tools@redhat.com.
Dusty